
The world of logistics is complex, and it involves various players in getting goods from one point to another. In recent years, terms like 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL have become increasingly common, but what do they mean, and how do they differ from each other? In this article, we will explore each of these terms and provide insights into their roles in logistics.
What is 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL?
1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL are acronyms used to describe different levels of supply chain management. While each term represents a different level of involvement in the logistics process, they all play a crucial role in ensuring that goods reach their intended destination.
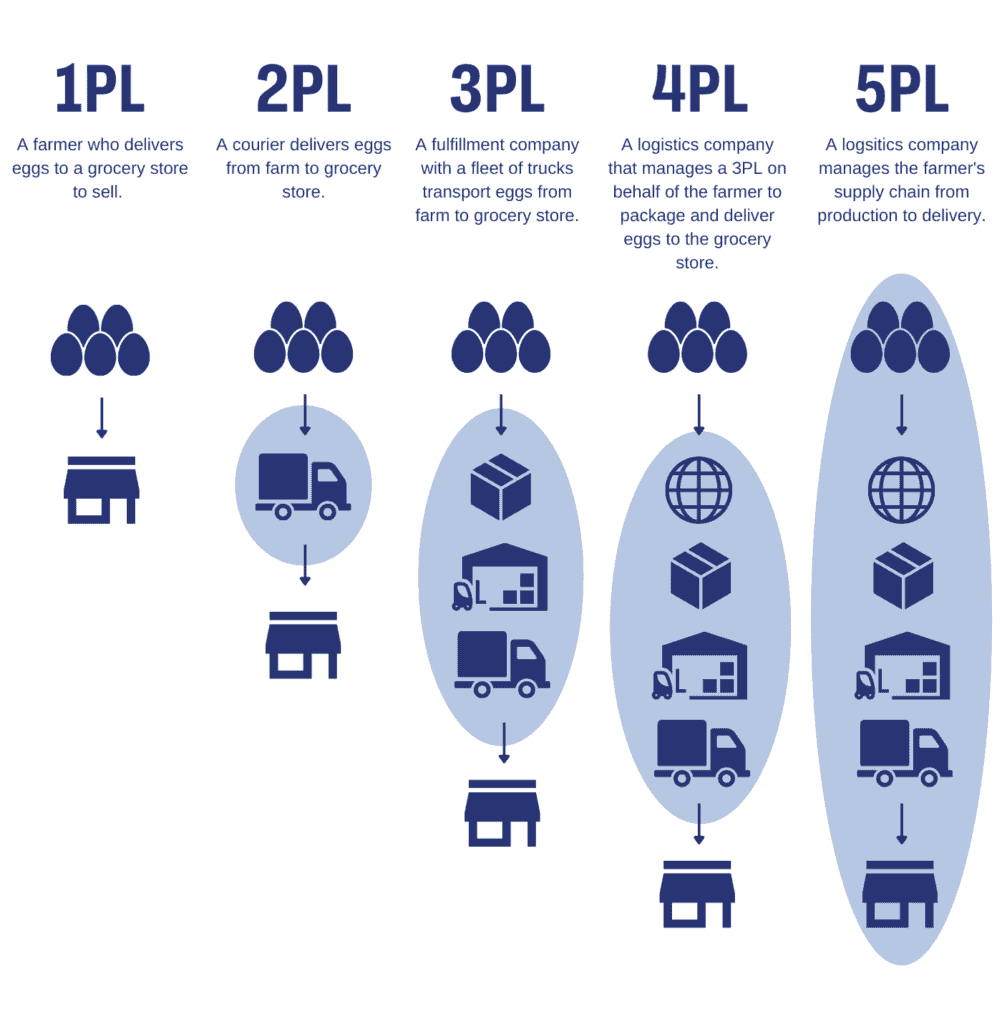
- 1PL stands for first-party logistics. It refers to a company that manages its logistics operations without outsourcing to a third-party logistics provider.
- 2PL stands for second-party logistics. It refers to a company that provides logistics services to another company but does not operate as a third-party logistics provider.
- 3PL stands for third-party logistics. It refers to a company that provides logistics services to other companies.
- 4PL stands for fourth-party logistics. It refers to a company that manages the logistics operations of another company.
- 5PL stands for fifth-party logistics. It refers to a company that manages the logistics operations of other logistics providers.
Each of these logistics models represents a different level of involvement in the supply chain management process. Understanding the role of each of these models is crucial to making informed decisions for your business.
Understanding the Role of 1PL in Logistics
1PL is also known as in-house logistics. It refers to a company that manages its logistics operations without outsourcing to a third-party logistics provider. In this model, the company is responsible for managing its transportation, warehousing, and distribution. The company owns and operates its logistics assets, such as trucks, warehouses, and distribution centers.
The 1PL model is suitable for businesses that have the resources and expertise to manage their logistics operations. It is common for manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers to use the 1PL model. The 1PL model provides businesses with complete control over their logistics operations, which allows them to customize their services to meet their specific needs.
However, the 1PL model is not suitable for all businesses. It requires significant investments in logistics assets, which can be costly. Additionally, managing logistics operations in-house can be time-consuming and can take the focus away from the core business. Businesses that do not have the resources or expertise to manage their logistics operations may benefit from outsourcing to a third-party logistics provider.
Understanding the Role of 2PL in Logistics
2PL refers to a company that provides logistics services to another company but does not operate as a third-party logistics provider. In this model, the logistics provider does not own any logistics assets, such as trucks, warehouses, or distribution centers. Instead, the logistics provider provides services such as transportation or warehousing to the company.
The 2PL model is suitable for businesses that require specialized logistics services but do not want to outsource their entire logistics operations to a third-party logistics provider. For example, a company may require specialized transportation services, such as refrigerated trucks, for transporting perishable goods. In this case, the company can outsource the transportation services to a 2PL provider.
The 2PL model provides businesses with access to specialized logistics services without having to invest in logistics assets. However, the 2PL model may not be suitable for businesses that require end-to-end logistics solutions.
Understanding the Role of 3PL in Logistics
3PL stands for third-party logistics. It refers to a company that provides logistics services to other companies. In this model, the logistics provider owns and operates logistics assets such as trucks, warehouses, and distribution centers. The logistics provider manages all aspects of logistics operations, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
The 3PL model is suitable for businesses that want to outsource their logistics operations to a third-party logistics provider. The 3PL provider has the expertise and resources to manage logistics operations efficiently. The 3PL provider can customize its services to meet the specific needs of the business.
The 3PL model provides businesses with access to logistics expertise and resources without having to invest in logistics assets. The 3PL provider can handle all aspects of logistics operations, which allows businesses to focus on their core competencies. However, the 3PL model may not be suitable for businesses that require complete control over their logistics operations.
Understanding the Role of 4PL in Logistics
4PL refers to a company that manages the logistics operations of another company. In this model, the 4PL provider does not own any logistics assets. Instead, the 4PL provider manages all aspects of logistics operations, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution. The 4PL provider acts as a single point of contact for all logistics operations.
The 4PL model is suitable for businesses that want to outsource their logistics operations to a company that specializes in supply chain management. The 4PL provider has the expertise and resources to manage logistics operations efficiently. The 4PL provider can customize its services to meet the specific needs of the business.
The 4PL model provides businesses with complete visibility and control over their logistics operations without having to invest in logistics assets. The 4PL provider can handle all aspects of logistics operations, which allows businesses to focus on their core competencies. However, the 4PL model may not be suitable for businesses that require complete control over their logistics operations.
Understanding the Role of 5PL in Logistics
5PL refers to a company that manages the logistics operations of other logistics providers. In this model, the 5PL provider acts as a single point of contact for all logistics operations. The 5PL provider manages all aspects of logistics operations, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
The 5PL model is suitable for businesses that want to outsource their logistics operations to a company that specializes in supply chain management. The 5PL provider has the expertise and resources to manage logistics operations efficiently. The 5PL provider can customize its services to meet the specific needs of the business.
The 5PL model provides businesses with complete visibility and control over their logistics operations without having to invest in logistics assets. The 5PL provider can handle all aspects of logistics operations, which allows businesses to focus on their core competencies. However, the 5PL model may not be suitable for businesses that require complete control over their logistics operations.
Differences between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL
The main differences between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL are the level of involvement in logistics operations and the ownership of logistics assets. 1PL manages its logistics operations in-house, while 2PL provides specialized logistics services without owning logistics assets. 3PL owns and operates logistics assets and manages logistics operations for other companies. 4PL manages logistics operations for other companies without owning logistics assets. 5PL manages the logistics operations of other logistics providers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Logistics Model
Each logistics model has its advantages and disadvantages. The 1PL model provides businesses with complete control over their logistics operations but requires significant investments in logistics assets. The 2PL model provides businesses with access to specialized logistics services but may not be suitable for businesses that require end-to-end logistics solutions. The 3PL model provides businesses with access to logistics expertise and resources without having to invest in logistics assets but may not be suitable for businesses that require complete control over their logistics operations. The 4PL and 5PL models provide businesses with complete visibility and control over their logistics operations without having to invest in logistics assets but may not be suitable for businesses that require complete control over their logistics operations.
Choosing the Right Logistics Model for Your Business
Choosing the right logistics model for your business depends on your specific needs and requirements. Businesses that have the resources and expertise to manage their logistics operations may benefit from the 1PL model. Businesses that require specialized logistics services may benefit from the 2PL model. Businesses that want to outsource their logistics operations to a third-party logistics provider may benefit from the 3PL model. Businesses that want to outsource their logistics operations to a company that specializes in supply chain management may benefit from the 4PL and 5PL models.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain and reduce costs. Each logistics model represents a different level of involvement in logistics operations and ownership of logistics assets. Choosing the right logistics model for your business depends on your specific needs and requirements. By understanding the role of each logistics model and the advantages and disadvantages of each, businesses can make informed decisions and optimize their supply chain management.
Image by Peter Lindenau from Pixabay



